Measles is one of the most easily spread infectious disease and it can have serious complications. Just being in the same room as someone with measles can result in transmission of infection. Measles is also known as rubeola and is NOT the same as German Measles (rubella).
Measles starts off like a bad cold and then the rash develops a few days later.
Preventing measles in children
The MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) and MMRV (measles, mumps, rubella and varicella) vaccination has virtually eliminated measles from Australia, however due to travel and the decline in immunisation this is something we need to be aware of in Australia. After 2 immunisations 99% of people are immune to measles.
Currently children receive MMR at 12 months and MMRV at 18 months according to the Australian National Immunisation Schedule. We answer all of your FAQ re immunisation here.
How measles is spread in kids
Measles is usually spread through the air after someone who is infected coughs or sneezes. It can also spread by direct contact with an infected person including touching their wounds or touching clothing with bodily fluid on it (urine, faeces etc)
People are contagious from 2 to 4 days BEFORE they get symptoms until 4 days after the rash appears.
Immunisation began in 1966, and so the majority of people born after this time have been vaccinated against measles.
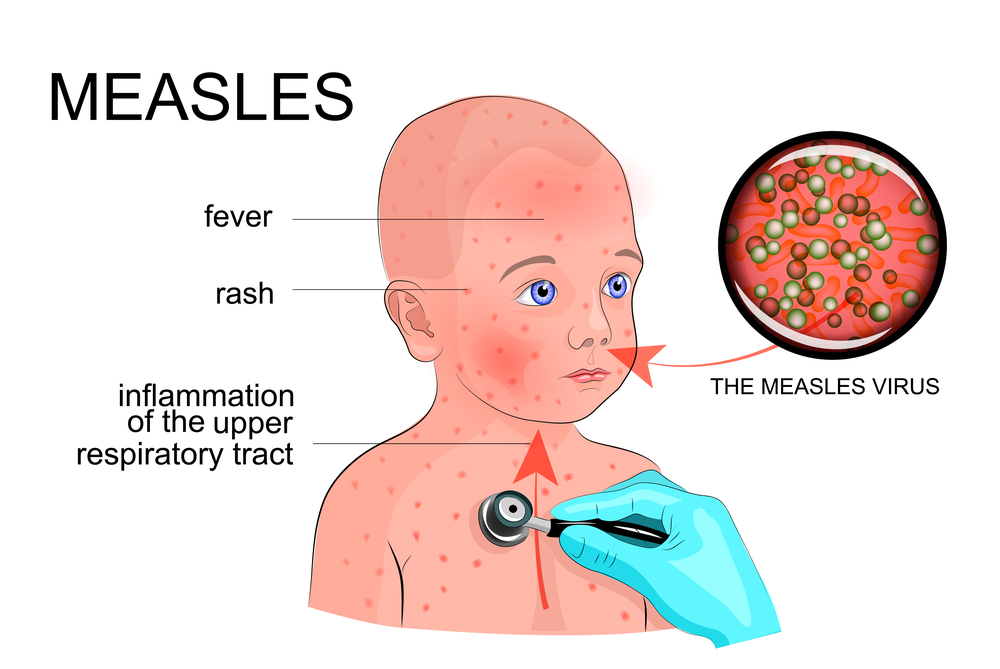
Symptoms of measles in children
After being exposed to measles it takes about 10 days for symptoms to appear and about 14 days for the measles rash to appear.
The first symptoms of measles are:
- fever
- tiredness
- runny nose and cough
- sore red eyes
Measles rash in children
The trademark symptom of measles is a red blotchy rash. The spots are not itchy and may be slightly raised. White spots inside the mouth can occur, called Koplik spots. The rash starts on the face for 1 to 2 days and spreads to the body lasting for 4 to 7 days.
Complications of measles
About 1/3 of people infected with measles will have a complication. Complications can be serious resulting in brain damage and occasionally death. These include
- ear infections
- diarrhoea
- pregnancy complications
- pneumonia
- About 1 in every 1000 people with measles develops encephalitis (swelling of the brain).
Confirming measles diagnosis
If you have measles symptoms, please contact your doctors office before you go in. It is highly contagious and they will follow a protocol to avoid the spread of the infection.
A blood test or a swab can be taken from the nose or throat and a urine sample are used to confirm the diagnosis of measles.
Treatment of measles in children
There is no available treatment for measles. Speak to your doctor to ensure you manage all symptoms. You need to rest, avoid contact with others and keep up your fluids. Complications will be managed by your doctor and treated individually.
Avoid spreading measles
It is VERY important to make sure you keep someone with measles or suspected of having measles away from other people for at least 4 days after the rash develops.
References
Measles immunisation information
General information